When Is The Best Time To Water Plants?
Understanding Plant Watering Needs
When is the best time to water plants – Proper watering is crucial for plant health and vitality. A plant’s water requirements are influenced by several key factors, and understanding these factors is the first step to successful plant care.
Factors Influencing Water Requirements
Several factors influence how often and how much you need to water your plants. These include sunlight exposure, soil type, pot size, and the plant’s species.
- Sunlight: Plants in direct sunlight dry out faster than those in shade. Increased sunlight necessitates more frequent watering.
- Soil Type: Well-draining soil allows excess water to escape, preventing root rot. Clay soils retain moisture longer than sandy soils.
- Pot Size: Smaller pots dry out quicker than larger ones. Smaller pots require more frequent watering.
- Plant Type: Different plants have different water requirements. Succulents store water in their leaves and need less frequent watering than ferns, which prefer consistently moist soil.
Signs of Underwatering and Overwatering
Recognizing the signs of underwatering and overwatering is essential for maintaining healthy plants. Symptoms vary depending on the plant type.
- Underwatering: Wilting leaves, dry soil, leaf browning or crisping (especially at the edges), stunted growth.
- Overwatering: Yellowing leaves, soggy soil, root rot (leading to a foul odor and wilting), leaf drop.
Watering Schedules for Common Houseplants
Here are some general watering schedules for common houseplants. Remember that these are guidelines, and actual watering needs will vary based on the factors discussed above.
- Succulents: Water thoroughly only when the soil is completely dry, usually every 2-4 weeks.
- Ferns: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Water more frequently, potentially every few days during warmer months.
- Snake Plants: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings, typically every 2-3 weeks.
Comparison of Water Needs
| Plant Type | Watering Frequency | Soil Moisture Preference | Signs of Overwatering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Succulents | Every 2-4 weeks (when soil is completely dry) | Dry to slightly moist | Soggy soil, yellowing leaves, root rot |
| Ferns | Every few days to weekly (depending on environment) | Consistently moist | Yellowing leaves, soggy soil, leaf drop |
| Snake Plants | Every 2-3 weeks (when soil is completely dry) | Dry between waterings | Yellowing leaves, soggy soil, root rot |
| Peace Lilies | When the top inch of soil is dry | Evenly moist | Yellowing leaves, drooping leaves, soggy soil |
The Role of Soil and Environment: When Is The Best Time To Water Plants

Source: thespruce.com
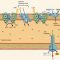
The soil and the surrounding environment play a significant role in determining a plant’s watering needs. Using the right soil and understanding environmental factors are key to successful plant care.
Importance of Well-Draining Soil
Well-draining soil is crucial for preventing root rot, a common problem caused by consistently wet soil. Excess water suffocates the roots, preventing them from absorbing oxygen and nutrients.
Soil Moisture Retention

Source: co.uk
Different soil types retain moisture at varying rates. Sandy soils drain quickly, requiring more frequent watering, while clay soils retain moisture for longer periods, potentially leading to overwatering if not managed properly.
Environmental Factors Affecting Watering Frequency
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and wind significantly impact how quickly soil dries out. Higher temperatures, lower humidity, and strong winds accelerate evaporation, increasing the frequency of watering.
Selecting Appropriate Pots and Ensuring Proper Drainage
Choosing the right pot and ensuring proper drainage are crucial aspects of plant care. Pots with drainage holes prevent waterlogging, while the pot size influences how quickly the soil dries out. Larger pots retain moisture longer than smaller ones.
- Drainage Holes: Essential for most plants to prevent root rot.
- Pot Size: Consider the plant’s mature size and root system when selecting a pot.
- Pot Material: Terracotta pots are porous and allow for better air circulation and evaporation, while plastic pots retain moisture longer.
Optimal Watering Techniques
Effective watering techniques are essential for plant health. Deep watering is preferred over frequent shallow watering, encouraging deep root growth and preventing shallow root systems prone to drought stress.
Best Practices for Watering Plants
Avoid overhead watering, which can lead to fungal diseases. Instead, water directly at the base of the plant, ensuring the soil is thoroughly moistened.
Comparing Watering Methods
Different watering methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Top watering is the most common method, while bottom watering allows for more even moisture distribution. Drip irrigation is a water-efficient method suitable for larger plantings.
- Top Watering: Simplest method, water directly onto the soil.
- Bottom Watering: Place the pot in a tray of water, allowing the soil to absorb moisture from the bottom.
- Drip Irrigation: A slow and efficient method that delivers water directly to the roots.
Checking Soil Moisture Levels
To determine if your plant needs watering, insert your finger about an inch into the soil. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water. If it feels moist, wait a few days before watering again.
Watering Different Plant Types

Source: quickcrop.ie
Watering techniques should be adjusted depending on the plant type and its growing habit. For hanging plants, water thoroughly, ensuring the water reaches all the roots. For large potted plants, water deeply and slowly to allow the water to penetrate the entire root ball.
Seasonal Considerations
Watering needs change throughout the year, influenced by seasonal variations in temperature, humidity, and sunlight. Adjusting your watering schedule according to the season is crucial for plant health.
Watering Needs During Different Seasons, When is the best time to water plants
During the active growing season (spring and summer), plants require more frequent watering due to increased evaporation and higher temperatures. During the dormant season (fall and winter), plants require less frequent watering because their growth slows down.
Impact of Seasonal Weather Patterns
Seasonal weather patterns significantly impact a plant’s hydration. Periods of high heat and low humidity require more frequent watering, while periods of rain may reduce the need for watering.
Adjusting Watering Schedules Based on Seasonal Changes
Adjust your watering schedule based on seasonal changes. For example, increase watering frequency during hot, dry summers and reduce watering frequency during cool, wet winters.
- Summer: Increase watering frequency due to higher temperatures and increased evaporation.
- Winter: Reduce watering frequency due to lower temperatures and reduced sunlight.
- Spring/Autumn: Adjust watering frequency based on temperature and rainfall.
Adjusting Watering Frequency Based on Temperature and Rainfall
- If temperatures are high and rainfall is low, increase watering frequency.
- If temperatures are low and rainfall is high, decrease watering frequency.
- Monitor soil moisture regularly to adjust watering accordingly.
Troubleshooting Watering Issues
Even with careful attention, watering problems can occur. Recognizing the symptoms of underwatering and overwatering is crucial for taking corrective action.
Common Watering Problems and Solutions
Common watering problems include yellowing leaves, wilting, and root rot. Yellowing leaves can indicate both underwatering and overwatering. Wilting often indicates underwatering, but can also be a sign of root rot in overwatered plants. Root rot is typically caused by overwatering and results in a foul odor and mushy roots.
Symptoms of Underwatering vs. Overwatering
Underwatering leads to dry, brittle soil, wilting leaves, and leaf browning. Overwatering results in soggy soil, yellowing leaves, and root rot.
Reviving an Underwatered or Overwatered Plant
For underwatered plants, water thoroughly and deeply. For overwatered plants, remove the plant from its pot, trim any rotten roots, and repot it in fresh, well-draining soil.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart can help guide you through troubleshooting steps for common plant watering issues. Start by checking the soil moisture level. If the soil is dry, water the plant. If the soil is wet, check for signs of root rot. If root rot is present, repot the plant in fresh soil.
If no root rot is present, adjust the watering schedule to prevent future problems.
FAQ Summary
What type of water should I use for my plants?
Tap water is generally fine, but allow it to sit for 24 hours to allow chlorine to dissipate. Rainwater is ideal, if available.
How often should I check my soil moisture?
Check soil moisture at least once a week, more frequently during hot, dry weather. Stick your finger about an inch into the soil; if it feels dry, it’s time to water.
The ideal time to water plants is generally early morning or late evening, to minimize evaporation. However, the cost of this essential care can vary significantly depending on your location and water source; for example, finding out how much does water plants cost in Russia might surprise you. Ultimately, consistent watering at the optimal time remains key to healthy plant growth.
My plant’s leaves are yellowing; what should I do?
Yellowing leaves can indicate overwatering or underwatering. Check the soil moisture; adjust watering accordingly. Ensure proper drainage.
Can I use ice cubes to water my plants?
While convenient, ice cubes can shock the roots. It’s better to water thoroughly with room-temperature water.