Nutritional Composition of Romaine Lettuce
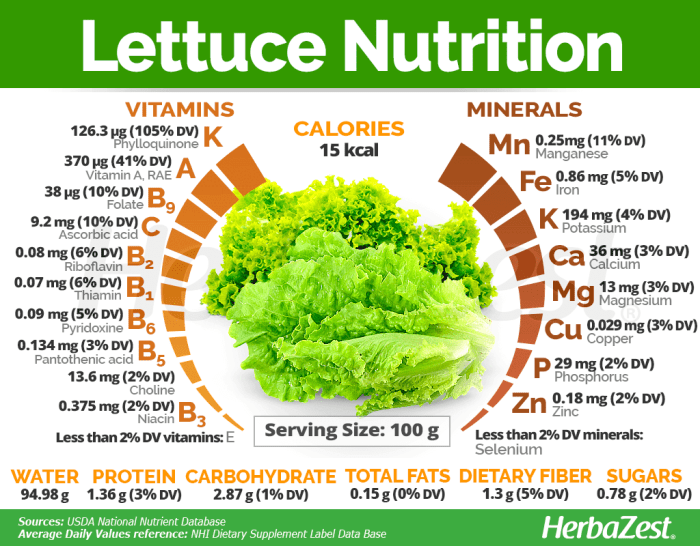
Romaine lettuce nutrition facts – Romaine lettuce, a crisp and refreshing leafy green, offers a surprising array of nutrients despite its low calorie count. It’s a versatile addition to salads, sandwiches, and wraps, providing a boost of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants with minimal impact on your daily caloric intake. Understanding its nutritional profile can help you appreciate its role in a balanced diet.
Macronutrient Breakdown in Romaine Lettuce
A typical cup (approximately 50g) of chopped romaine lettuce contains a small amount of carbohydrates, a negligible amount of protein, and virtually no fat. The majority of its carbohydrate content comes from fiber, which plays a crucial role in digestive health. Specifically, one cup of romaine provides roughly 1 gram of carbohydrates, with about 0.8 grams being dietary fiber.
The protein content is minimal, around 0.3 grams per cup. Fat content is less than 0.1 grams per cup. This low-calorie, high-fiber profile makes romaine lettuce an excellent choice for those watching their weight or seeking to increase their fiber intake.
Vitamin and Mineral Content of Romaine Lettuce
Romaine lettuce is a rich source of several essential vitamins and minerals. These contribute significantly to various bodily functions, promoting overall health and well-being. The following table provides a detailed overview of its key nutritional components:
| Nutrient | Amount per Cup (approx. 50g) | % Daily Value (DV) | Role in Human Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 10% DV | Supports vision, immune function, and cell growth. | |
| Vitamin C | 3% DV | Acts as an antioxidant, boosts the immune system, and aids in collagen production. | |
| Vitamin K | 20% DV | Essential for blood clotting and bone health. | |
| Folate | 5% DV | Crucial for cell growth and development, particularly important during pregnancy. | |
| Potassium | 4% DV | Helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance. | |
| Calcium | 3% DV | Essential for bone health and muscle function. | |
| Magnesium | 2% DV | Plays a role in muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation. |
*Note: Daily Values (DV) are based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Individual needs may vary.*
Phytonutrients and Antioxidants in Romaine Lettuce
Romaine lettuce contains various phytonutrients and antioxidants, which contribute to its potential health benefits. These compounds help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Examples include beta-carotene (a precursor to vitamin A), lutein, and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for eye health. These carotenoids, along with other antioxidants present in romaine lettuce, may contribute to a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Further research continues to explore the full extent of these beneficial compounds and their impact on human health.
Romaine Lettuce and Calorie Content
Romaine lettuce is a popular choice for salads and other dishes, largely due to its crisp texture and slightly bitter taste. Beyond its culinary appeal, however, lies its significant nutritional value, particularly its remarkably low calorie content. Understanding this aspect is crucial for those seeking to manage their weight or simply maintain a healthy diet. This section will delve into the calorie count of romaine lettuce, comparing it to other lettuces and exploring its impact on weight management.Romaine lettuce boasts an exceptionally low calorie density.
A typical serving, approximately one cup of chopped romaine, contains only about 8 calories. This makes it an ideal addition to any diet focused on calorie control. The low calorie count stems from its high water content and relatively low levels of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This contrasts sharply with some higher-calorie foods, making it a beneficial choice for individuals aiming to reduce their overall caloric intake.
Calorie Comparison of Common Lettuces
The following table provides a direct comparison of the calorie content of romaine lettuce against other common types, highlighting romaine’s low-calorie advantage. These values are approximate and can vary slightly depending on factors like growing conditions and measurement methods. However, they represent a general comparison useful for dietary planning.
| Lettuce Type | Calories per Cup (chopped) | Serving Size Notes | Dietary Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Romaine Lettuce | 8 | Approximately 1 cup chopped | Excellent low-calorie option for salads and other dishes. |
| Iceberg Lettuce | 10 | Approximately 1 cup chopped | Slightly higher in calories than romaine, but still a low-calorie choice. |
| Spinach | 7 | Approximately 1 cup chopped | Similar calorie count to romaine, offering additional nutritional benefits. |
Impact of Romaine Lettuce’s Low Calorie Density on Weight Management
The low calorie density of romaine lettuce significantly contributes to its role in weight management strategies. By incorporating romaine into meals, individuals can increase their food volume without significantly increasing their caloric intake. This helps promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and contributing to a calorie deficit, which is essential for weight loss. For example, substituting a higher-calorie snack with a large romaine lettuce salad can significantly reduce daily caloric intake without sacrificing feelings of fullness.
This approach allows for greater flexibility and satisfaction in dietary choices while supporting weight management goals.
Potential Risks and Considerations

While romaine lettuce offers numerous nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks associated with its consumption. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safety measures can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing negative health consequences. This section will address potential foodborne illnesses, medication interactions, and safe handling practices.
Romaine lettuce, a nutritional powerhouse, offers a low-calorie, high-vitamin option for a healthy diet. Comparing its nutritional profile to something like a digoirno regular pizza nutrition facts highlights the stark contrast in caloric density and nutrient content. Ultimately, understanding both profiles helps make informed choices about balanced nutrition.
One of the most significant risks associated with eating romaine lettuce is the potential for foodborne illnesses. Outbreaks of Escherichia coli ( E. coli) and other bacterial contaminations have been linked to romaine lettuce in the past, resulting in serious illnesses, hospitalizations, and, in rare cases, death. These outbreaks highlight the importance of careful sourcing, handling, and preparation of this leafy green.
Romaine Lettuce and Foodborne Illnesses
Contamination can occur at various stages of the romaine lettuce production process, from the farm to the consumer’s kitchen. Factors such as improper irrigation, animal fecal contamination, and inadequate sanitation practices can introduce harmful bacteria. Symptoms of E. coli infection can range from mild diarrhea and abdominal cramps to severe dehydration and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a life-threatening complication that can cause kidney failure.
Therefore, choosing romaine lettuce from reputable sources and practicing thorough washing are essential preventative measures.
Romaine Lettuce and Medication Interactions
There is limited evidence suggesting direct interactions between romaine lettuce and specific medications. However, individuals with specific health conditions or those on certain medications should consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice. For example, individuals with vitamin K deficiencies, who might be on anticoagulant medications, should be aware of the vitamin K content in romaine lettuce and discuss appropriate intake levels with their doctor, as this vitamin can affect blood clotting.
Safe Handling and Storage of Romaine Lettuce
Proper handling and storage are critical in minimizing the risk of contamination. Washing romaine lettuce thoroughly under running water before consumption is paramount. Discard any outer leaves that appear damaged or wilted. Store romaine lettuce in a sealed container in the refrigerator to maintain its freshness and prevent bacterial growth. Do not leave romaine lettuce at room temperature for extended periods, as this can promote the rapid multiplication of harmful bacteria.
Discard any romaine lettuce that shows signs of spoilage, such as discoloration or slimy texture.
Romaine Lettuce and Food Safety
Ensuring the safety of your romaine lettuce is crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses. Proper selection, washing, and storage techniques significantly reduce the risk of contamination and extend the shelf life of this nutritious leafy green. Following these guidelines will help you enjoy romaine lettuce safely and confidently.
Selecting fresh, high-quality romaine lettuce begins at the grocery store. Look for heads that are firm, crisp, and free from bruises or discoloration. The leaves should be a vibrant, deep green color, and avoid any wilted or yellowing leaves. Check the base of the head; it should be firm and not slimy. If purchasing pre-washed or pre-cut romaine, ensure the packaging is intact and free from damage, and check the expiration date.
Guidelines for Selecting Fresh Romaine Lettuce
Choosing romaine lettuce carefully at the store is the first step in ensuring its safety and quality. Examine each head thoroughly before purchasing, paying close attention to its appearance and firmness.
Safe Washing and Preparation of Romaine Lettuce, Romaine lettuce nutrition facts
Thorough washing is essential to remove any potential contaminants, such as soil, bacteria, or pesticides. Improper washing can lead to foodborne illnesses. The following steps provide a safe and effective method.
- Remove any outer, damaged leaves.
- Rinse the romaine lettuce thoroughly under cold, running water. Gently separate the leaves to ensure all surfaces are cleaned.
- Consider soaking the lettuce in a bowl of cold water with a small amount of food-grade vinegar (about 1 tablespoon per quart of water) for 10-15 minutes. This can help remove any lingering pesticides or bacteria.
- Rinse the lettuce again with cold water and allow it to drain completely before using or storing.
- For pre-cut romaine, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for washing and preparation.
Proper Refrigeration and Storage of Romaine Lettuce
Proper storage is vital for maintaining the freshness and safety of romaine lettuce. Improper storage can lead to spoilage and increase the risk of bacterial growth.
To maximize the shelf life and safety of your romaine lettuce, store it in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator. Wrap the whole head loosely in a paper towel or place it in a loosely sealed plastic bag to prevent moisture buildup. Pre-washed and pre-cut lettuce should be stored according to the package instructions, usually in a sealed container or bag.
Avoid storing it with fruits that emit ethylene gas, such as apples and bananas, as this can accelerate spoilage. Discard any romaine lettuce that shows signs of wilting, discoloration, or slime.
FAQ Corner: Romaine Lettuce Nutrition Facts
Is romaine lettuce good for weight loss?
Yes! Its low calorie and high fiber content promotes satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer and potentially aiding in weight management.
Can I eat romaine lettuce every day?
Moderation is key with any food. Daily consumption is fine as part of a balanced diet, but variety is always recommended.
How long can I store romaine lettuce?
Properly stored in the refrigerator, romaine lettuce can last for about a week. Look for crisp leaves and avoid any wilting or discoloration.
Is it okay to eat romaine lettuce raw?
Yes, romaine is best enjoyed raw to preserve its nutritional value. However, make sure to wash it thoroughly!
