How Do You Plant Water Lilies?
Choosing the Right Water Lily: How Do You Plant Water Lilies
How do you plant water lilies – Selecting the appropriate water lily variety is crucial for successful cultivation. Consider your pond’s size, climate, and sunlight exposure to ensure the chosen lily thrives. Different varieties offer diverse characteristics in terms of size, flower color, and hardiness.
Water Lily Variety Comparison
The following table compares several popular water lily varieties. Note that growth characteristics can vary slightly depending on growing conditions.
| Variety | Size (Diameter) | Flower Color | Hardiness Zones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nymphaea ‘Attraction’ | Medium (3-4 feet) | Deep Pink | 4-11 |
| Nymphaea ‘Alba’ | Large (4-6 feet) | White | 4-11 |
| Nymphaea ‘Perry’s Baby Red’ | Small (1-2 feet) | Red | 5-11 |
| Nymphaea ‘Blue Beauty’ | Medium (3-4 feet) | Blue | 5-11 |
Factors Influencing Water Lily Selection
Choosing a water lily involves considering pond size, climate, and sunlight. Smaller ponds suit smaller varieties, while larger ponds accommodate larger ones. Hardiness zones dictate which lilies will survive winter temperatures. Sunlight requirements vary; some need full sun, while others tolerate partial shade.
Water Lily Selection Flowchart
This flowchart helps guide the decision-making process for choosing a suitable water lily.
(Visual description of a flowchart: Start -> Pond Size (Small/Medium/Large) -> Climate (Hardy/Moderate/Tropical) -> Sunlight (Full Sun/Partial Shade) -> Choose Water Lily Variety based on previous selections -> End)
Preparing the Planting Container
The choice and preparation of the planting container significantly impact the water lily’s health and growth. Proper drainage and aeration are essential to prevent root rot and ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
Container Selection and Preparation
- Select a container at least 12 inches in diameter and depth, preferably larger for bigger lilies.
- Use a sturdy, non-toxic material like plastic, fiberglass, or even a sturdy woven basket.
- Ensure the container has adequate drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
- Clean the container thoroughly to remove any debris or contaminants.
Drainage and Aeration
Good drainage prevents waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. Aeration ensures oxygen reaches the roots, promoting healthy growth. A layer of gravel or rocks at the bottom of the container enhances both drainage and aeration.
Adding Gravel or Rocks
Place a 2-3 inch layer of gravel or small rocks at the bottom of the container before adding soil. This layer improves drainage and provides a stable base for the soil and rhizome.
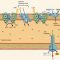
Planting the Water Lily
Proper planting technique is essential for establishing a healthy water lily. Gentle handling of the rhizome and correct planting depth are crucial for successful growth.
Planting Procedure

Source: wordpress.com
- Carefully remove the water lily from its packaging, ensuring the rhizome remains intact.
- Fill the container partially with a high-quality aquatic planting mix.
- Place the rhizome horizontally on top of the soil, ensuring the growing points (eyes) face upwards.
- Cover the rhizome with the remaining soil, leaving the growing points exposed.
- Water thoroughly but avoid overwatering.
Visual Description of a Properly Planted Water Lily
A properly planted water lily shows the rhizome lying horizontally, partially buried in the soil mix with the growing points facing upwards. The soil level should be just below the rim of the container.
Potential Planting Problems and Solutions
Common issues include damaged rhizomes (solution: carefully repair or remove damaged parts) and improper planting depth (solution: adjust soil level to expose growing points).
Positioning the Water Lily in the Pond
Optimal placement ensures sufficient sunlight and appropriate water depth for healthy growth and abundant flowering. Adjusting the position and depth is crucial for adapting to changing conditions.
Sunlight Exposure and Water Depth
Water lilies need adequate sunlight for flowering. The ideal water depth varies depending on the variety, but generally ranges from 1 to 4 feet.
Sunlight Effects on Water Lily Growth
| Sunlight Level | Flowering | Leaf Growth | Overall Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Sun (6+ hours) | Abundant | Vigorous | Excellent |
| Partial Shade (4-6 hours) | Moderate | Good | Good |
| Shade (Less than 4 hours) | Sparse | Weak | Poor |
Adjusting Water Depth

Source: hdnux.com
Adjust the water depth by adding or removing water or by adjusting the container’s position in the pond. Ensure the water depth is suitable for the chosen variety.
Ongoing Care and Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures a healthy and thriving water lily. This includes fertilization, removal of dead leaves, and monitoring for pests and diseases.
Maintenance Schedule
- Fertilize every 4-6 weeks during the growing season using a water lily specific fertilizer.
- Remove dead or decaying leaves promptly to prevent disease.
- Inspect regularly for signs of pests or diseases.
Common Water Lily Problems and Solutions
Common problems include aphids (solution: use insecticidal soap), fungal diseases (solution: improve air circulation and avoid overwatering), and algae (solution: maintain water clarity).
Visual Description of a Healthy Water Lily
A healthy water lily displays vibrant green leaves, abundant blooms, and strong, healthy rhizomes. The leaves are free from blemishes or pests and the blooms are numerous and vibrant.
Wintering Water Lilies (For Temperate Climates)
In temperate climates, protecting water lilies from freezing temperatures is crucial for their survival. Several methods exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Planting water lilies involves selecting a suitable pond and ensuring sufficient sunlight. The rhizomes should be placed in rich soil, and the depth depends on the variety. Interestingly, proper watering techniques extend beyond aquatic plants; understanding how often to water a spider plant, as detailed in this helpful guide: how often to water a spider plant , can offer insights into the general principles of plant hydration.
Returning to water lilies, consistent monitoring of water levels and nutrient balance is key to their flourishing.
Winter Protection Methods
- Bringing the container indoors: This offers the best protection but requires space and access to a suitable location.
- Insulating the pond: This involves covering the pond with insulating materials to prevent the water from freezing completely.
- Moving the container to a sheltered location: This can involve moving the container to a warmer, more protected part of the pond or garden.
Comparison of Wintering Techniques, How do you plant water lilies
Bringing containers indoors provides the most reliable protection, while insulating the pond is less labor-intensive but may not be as effective in extremely cold climates. Moving the container to a sheltered location offers a compromise between these two methods.
Protecting Rhizomes from Freezing
The rhizomes are the most vulnerable part of the water lily during winter. Protecting them from freezing temperatures is crucial for the plant’s survival. Methods include insulating the container or moving it to a frost-free environment.
Questions and Answers
Can I plant water lilies in a pot directly in the pond, without a separate container?
While possible, it’s generally not recommended. A separate container allows for easier maintenance, including cleaning, fertilization, and overwintering.
How often should I fertilize my water lilies?
Fertilizing frequency depends on the lily variety and the nutrient levels in your pond water. A slow-release fertilizer pellet placed at planting time is often sufficient, with occasional supplemental feeding during the growing season as needed.
What should I do if my water lilies aren’t blooming?
Insufficient sunlight, improper planting depth, nutrient deficiencies, or pest infestations can all inhibit blooming. Review your planting setup and consider addressing these potential issues.
How do I prevent algae growth around my water lilies?
Maintain proper water balance and avoid over-fertilizing. Regular pond maintenance, including removing excess algae and debris, will also help.